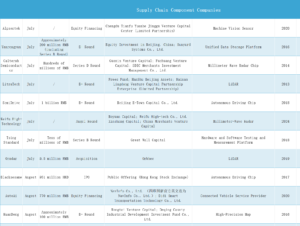
With technological advancements and growing market demand, the autonomous urban logistics sector is gradually emerging as a new battleground in the logistics industry. E-commerce giants like Cainiao and JD Logistics have entered the space, introducing new dynamics to the competition.
Cainiao has revealed that before this year’s Singles’ Day shopping festival, it received orders for autonomous delivery vehicles from customers in seven provinces across China. In Hangzhou, Cainiao’s autonomous vehicles have already expanded their fleet at some locations. Before Singles’ Day, one logistics site in Yuhang District operated over 20 autonomous vehicles, handling approximately 55% of the site’s workload. As the festival approached, the site ordered more vehicles, increasing the fleet size to 30, making it the largest autonomous vehicle fleet at a single location nationwide.

Moreover, this year, Cainiao fully integrated with JD’s platform following JD Logistics’ earlier integration with Taobao and Tmall. JD Logistics has also been intensifying its research into autonomous technology, exploring new models such as logistics automation. In August, JD Logistics unveiled its sixth-generation autonomous delivery vehicle equipped with advanced perception models and announced plans to deploy over 200,000 autonomous delivery vehicles within the next three years.

E-commerce Giants Invest in Autonomous Urban Logistics
The involvement of these e-commerce giants in the autonomous delivery sector dates back to 2016.
Cainiao introduced its first-generation last-mile delivery robot, “Little G,” in 2016, and tested it in various scenarios, such as campuses and communities. In 2020, Alibaba’s DAMO Academy merged its autonomous driving lab with Cainiao’s autonomous logistics vehicle R&D team to launch the “Xiaomanlv” logistics vehicle. This fully autonomous delivery vehicle, equipped with Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB), began regular operations at over 200 universities across China.
Since then, Cainiao’s autonomous vehicles have expanded into more provinces, servicing cities and universities nationwide. Beyond semi-enclosed areas, these vehicles have been tested in business districts, industrial parks, and other settings, with the company exploring partnerships with e-commerce platforms, courier companies, and retailers.
Similarly, JD Logistics has been committed to autonomous driving technology since 2016, becoming the first company in China to apply autonomous driving in logistics. In June 2017, JD’s autonomous delivery robot completed its first delivery task. Over the years, JD has introduced several generations of intelligent delivery vehicles, each with technical advancements.
Currently, JD Logistics’ autonomous delivery vehicles operate in nearly 30 cities, covering tasks such as last-mile delivery in residential areas and unmanned rapid delivery in shopping districts. In Q1 2024, JD reported a year-on-year increase of over 100% in supermarket delivery orders fulfilled by autonomous vehicles, highlighting the rapid growth of its autonomous delivery business.
For giants that “know logistics, technology, and innovation,” their robust logistics networks and superior service capabilities provide a natural advantage for large-scale deployment of autonomous vehicles.

Opportunities and Challenges for Autonomous Driving Companies
Apart from internet giants like JD and Alibaba, another major player in the autonomous delivery market comprises emerging tech-driven companies specializing in midstream solutions. These companies, such as Haomo.AI, Zelos, Zhishuo Technology, Rino.AI, and NEOLIX, leverage their flexibility and innovation to seize opportunities in specific niches or targeted markets.
For instance, Haomo.AI partnered with Dmall for product delivery as early as 2021 and expanded its reach by collaborating with Dada Express in 2022, covering use cases like parcel drop-offs, campus delivery, and smart communities. Its flagship product has evolved to its third generation, with the “Little Magic Camel 3.0” being the world’s first mid-sized last-mile autonomous delivery vehicle priced under 90,000 RMB. In Q3 2024, Haomo joined forces with Dada Now for supermarket deliveries in Shanghai’s Pudong district. As of October, Haomo’s autonomous delivery vehicles have completed over 820,000 orders across supermarkets and courier services.
This demonstrates that with technical innovation and precise market positioning, autonomous driving companies can achieve success in specific scenarios.
In June, Zelos unveiled four L4-level autonomous vehicles — Z2, Z5, Z8, and Z10 — as part of a comprehensive urban logistics solution for low-speed applications. The Z2 is a compact platform designed for narrow-road scenarios like campuses, residential areas, and warehouses, while the Z8 and Z10 feature industry-leading payload capacity and range, suitable for tasks like dock transfers, industrial logistics, and long-distance transportation. On the launch day, Neolix reportedly sold six months’ worth of production capacity within an hour.

For companies like Haomo and NEOLIX, mass production capabilities are key to securing their position in the downstream value chain.
Founded in 2018, NEOLIX established an L4 autonomous vehicle factory in Changzhou capable of producing 10,000 units annually. Similarly, in 2020, Haomo launched its StarLoop Factory in Baoding, a flexible production base for last-mile autonomous delivery vehicles with an annual capacity of 10,000 units. Zhishuo Technology has built a factory in Liu’an, Anhui, with a yearly production capacity of 20,000 vehicles. These production capabilities demonstrate that autonomous driving companies are well-prepared to meet the demands of large-scale deployment.
As technology matures and costs decrease, the commercialization of autonomous delivery vehicles is becoming increasingly feasible. Government support for autonomous driving technology and improvements in regulatory frameworks further create favorable conditions for scaling up commercial operations.

Conclusion
The entry of giants like Cainiao and JD into the autonomous urban logistics sector undoubtedly introduces new challenges. However, it also opens up opportunities for collaboration and expanded market potential for autonomous driving companies. With continuous technological advancements and market growth, the future of autonomous urban logistics holds limitless possibilities.